Bacterial cell wall staining pdf
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
The cell wall of most bacteria has an overall net negative charge and thus can be stained directly with a single basic (positively charged) stain or dye. This type of stain allows us to observe the shape, size and arrangement of bacteria.
Relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction. 37 . 38 Bacterial Cell Wall • Peptidoglycan (murein) –rigid structure that lies just outside the cell plasma membrane –two types based on Gram stain •Gram-positive: stain purple; thick peptidoglycan •Gram-negative: stain pink or red; thin peptidoglycan and outer membrane . 39 Cell Wall Functions • Maintains shape
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram+ and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram+ bacteria. 4. Gram+ bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
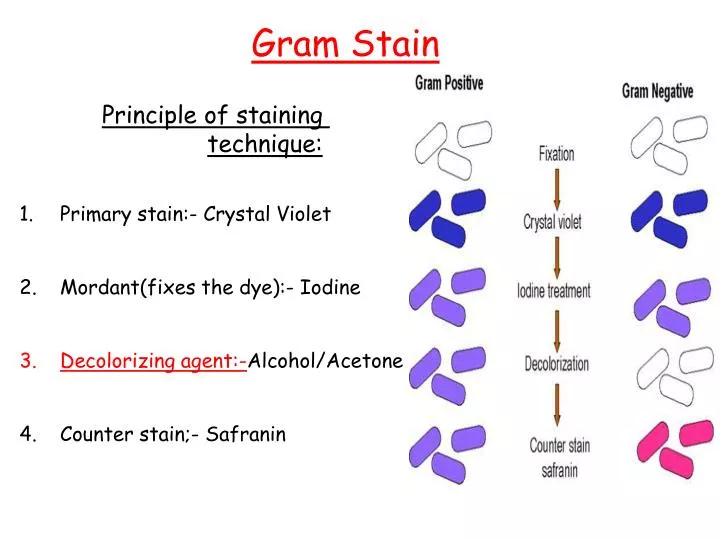
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria Cell Walls Microbiology Open Oregon State

Phloxine B a versatile bacterial stain Rasooly – 2007
staining; and 3) will retain the original cell morphology after fixation and staining. After you have stained your bacterial smears, you will examine them with the oil immersion lens, noting the morphological and staining characteristics of each species.
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
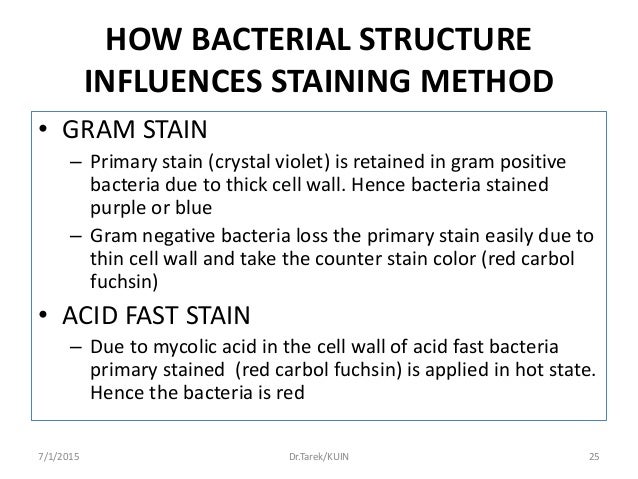
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionic (negative charge). Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on

Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting the properties of peptidoglycan. Gram staining method is useful in differentiating majority of bacterial species into two broad categories. Even though all bacterial species cannot be differentiated based on gram staining technique, this method has immense application in clinical
The differential Gram stain gives additional information about the bacterial cell wall, which may be Gram positive (the deep purple color of crystal violet), or Gram negative (the pink color of the counterstain safranin).
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
about the characteristics of the cell wall (Thickness). Gram staining (or Gram’s Gram staining (or Gram’s method) is an emprical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large
Isolation and Solubilization of Gram-Positive Bacterial
Gram-staining Properties The structural format and chemical composition of bacterial cell walls dictate the staining response of cells to the Gram stain. 7 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www. Sphaerotilus.
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells – advantages and disadvantages of non renewable energy pdf staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Gram negative bacteria have cell wall generally thinner than those of gram positive bacteria. Gram negative ones have higher lipid content than the gram positive bacteria.
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
Peptidoglycan (murein) is the principal component of the bacterial cell wall and it is responsible for the shape and extreme tough nature of the cell wall. Based on the characteristics of the cell wall, the bacterial cells are classified into Gram Positive and Gram Negative , primarily based on the classical staining reaction called Gram Staining.
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
Gram positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. In effect, the cell wall traps the crystal violet in the cytoplasm, concealing the red dye safranin in gram staining experiment.
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
Prokaryotes (bacteria) and Gram Staining Gram positive and Gram negative. BTEC101, Day 5 Why are we learning this? We will be monitoring our bioreactors for bacterial contamination. We sometimes are culturing E.coli as the organism of choice and in this case we want to make sure it is not contaminated. BTEC101, Day 5 Mycoplasmas Mycoplasmas small prokaryotes without a cell wall. …
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
All bacteria are Prokaryotes csus.edu

Techniques of bacterial taxonomy WDCM
Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for


Gram Staining Bacteria Cell Wall By Wasim Arsal YouTube
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
application form renewal indian passport melbourne – Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com


Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
Bacteria Cell Walls Microbiology Open Oregon State
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
staining; and 3) will retain the original cell morphology after fixation and staining. After you have stained your bacterial smears, you will examine them with the oil immersion lens, noting the morphological and staining characteristics of each species.
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionic (negative charge). Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting the properties of peptidoglycan. Gram staining method is useful in differentiating majority of bacterial species into two broad categories. Even though all bacterial species cannot be differentiated based on gram staining technique, this method has immense application in clinical
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
Gram positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. In effect, the cell wall traps the crystal violet in the cytoplasm, concealing the red dye safranin in gram staining experiment.
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
Gram Staining Bacteria Cell Wall By Wasim Arsal YouTube
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
about the characteristics of the cell wall (Thickness). Gram staining (or Gram’s Gram staining (or Gram’s method) is an emprical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
Peptidoglycan (murein) is the principal component of the bacterial cell wall and it is responsible for the shape and extreme tough nature of the cell wall. Based on the characteristics of the cell wall, the bacterial cells are classified into Gram Positive and Gram Negative , primarily based on the classical staining reaction called Gram Staining.
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
Gram-staining Properties The structural format and chemical composition of bacterial cell walls dictate the staining response of cells to the Gram stain. 7 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www. Sphaerotilus.
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
staining; and 3) will retain the original cell morphology after fixation and staining. After you have stained your bacterial smears, you will examine them with the oil immersion lens, noting the morphological and staining characteristics of each species.
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC Scribd
Bacterial cells.pdf Bacteria Staining Scribd
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Gram negative bacteria have cell wall generally thinner than those of gram positive bacteria. Gram negative ones have higher lipid content than the gram positive bacteria.
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
Gram positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. In effect, the cell wall traps the crystal violet in the cytoplasm, concealing the red dye safranin in gram staining experiment.
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
staining; and 3) will retain the original cell morphology after fixation and staining. After you have stained your bacterial smears, you will examine them with the oil immersion lens, noting the morphological and staining characteristics of each species.
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
Bacteria Cell Walls Microbiology Open Oregon State
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
Gram negative bacteria have cell wall generally thinner than those of gram positive bacteria. Gram negative ones have higher lipid content than the gram positive bacteria.
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram bacteria. 4. Gram bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
Bacterial Staining Free Essays PhDessay.com
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Isolation and Solubilization of Gram-Positive Bacterial
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
Gram negative bacteria have cell wall generally thinner than those of gram positive bacteria. Gram negative ones have higher lipid content than the gram positive bacteria.
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
Bacterial cells.pdf Bacteria Staining Scribd
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
Gram negative bacteria have cell wall generally thinner than those of gram positive bacteria. Gram negative ones have higher lipid content than the gram positive bacteria.
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram bacteria. 4. Gram bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
Gram positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. In effect, the cell wall traps the crystal violet in the cytoplasm, concealing the red dye safranin in gram staining experiment.
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy WDCM
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
The cell wall of most bacteria has an overall net negative charge and thus can be stained directly with a single basic (positively charged) stain or dye. This type of stain allows us to observe the shape, size and arrangement of bacteria.
Gram-staining Properties The structural format and chemical composition of bacterial cell walls dictate the staining response of cells to the Gram stain. 7 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www. Sphaerotilus.
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
The cell wall of most bacteria has an overall net negative charge and thus can be stained directly with a single basic (positively charged) stain or dye. This type of stain allows us to observe the shape, size and arrangement of bacteria.
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
Gram-staining Properties The structural format and chemical composition of bacterial cell walls dictate the staining response of cells to the Gram stain. 7 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www. Sphaerotilus.
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
Dyes for Living Cell Staining If the reagent is in a solid form, use DMSO to prepare a solution with a certain concentration. Since CFSE has a succinimidyl group, the stability of the prepared DMSO solution is poor. After the preparation of the DMSO solution, aliguot in an appropri-
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
staining; and 3) will retain the original cell morphology after fixation and staining. After you have stained your bacterial smears, you will examine them with the oil immersion lens, noting the morphological and staining characteristics of each species.
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
Gram-staining Properties The structural format and chemical composition of bacterial cell walls dictate the staining response of cells to the Gram stain. 7 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www. Sphaerotilus.
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram bacteria. 4. Gram bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting the properties of peptidoglycan. Gram staining method is useful in differentiating majority of bacterial species into two broad categories. Even though all bacterial species cannot be differentiated based on gram staining technique, this method has immense application in clinical
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the dye to the cell wall. 0 Coca in clusters – staphylococci 0 Coca in chains – thyrotrophic 2. A.
Bacteria Cell Walls Microbiology Open Oregon State
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
about the characteristics of the cell wall (Thickness). Gram staining (or Gram’s Gram staining (or Gram’s method) is an emprical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting the properties of peptidoglycan. Gram staining method is useful in differentiating majority of bacterial species into two broad categories. Even though all bacterial species cannot be differentiated based on gram staining technique, this method has immense application in clinical
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionic (negative charge). Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
Bacteria Cell Walls Microbiology Open Oregon State
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
Size of Bacteria • Unit of measurement in bacteriology is the micron (micrometre, µm) • Bacteria of medical importance (0.2 – 1.5 µm) in diameter (3
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
• Bacteria are classified by their Gram stain characteristics. • Gram staining is the application of a crystal violet dye to a culture of bacteria. Bacteria that retain the color of the dye are called Gram positive; bacteria that don’t are Gram negative. – The Gram stain attaches to peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. • In Gram-negative bacteria, the peptidoglycan layer is
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
Cell Wall Staining Procedure Napa Valley College
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 Stain Technology Vol 28 No 4
Peptidoglycan (murein) is the principal component of the bacterial cell wall and it is responsible for the shape and extreme tough nature of the cell wall. Based on the characteristics of the cell wall, the bacterial cells are classified into Gram Positive and Gram Negative , primarily based on the classical staining reaction called Gram Staining.
between a positively charged color ion and the negatively charged bacterial cell. In the In the Direct or Positive Staining Procedure a cell takes up a positively charged dye and
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
A bacterial staining method using fluorescent dye is a popular tool, although the weakness of fluorescence intensity and its fading over time constitute notable drawbacks. In the process of esterase-active bacteria staining with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA),
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 Stain Technology Vol 28 No 4
Introduction. Cell wall staining technique is a special staining technique in which we especially stain the cell wall of the bacterial cell. As we know cell wall is the outer most rigid covering of cell and depending upon the structure of cell wall bacterial cell are classified in Gram positive and Gram negative cells.
1. Bacterial cell structure Cells are of two types: On the basis of the response of the bacterial cell wall with gram stain, the bacterial cell walls can be classified as “ gram positive” or “ gram negative”. For both the gram positive and . 4 gram negative bacteria, particles of approximately 2 nm can pass through the peptidoglycan [2]. Figure 2. Schematic diagram of bacterial
about the characteristics of the cell wall (Thickness). Gram staining (or Gram’s Gram staining (or Gram’s method) is an emprical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
Physical and biochemical surface properties of Gram-positive bacteria in relation to adhesion to bovine mammary cells and tissues A review of the literature W. MAMO * Summary: Functional properties of cell-wall components of Gram-positive bacteria and outer cell-wall structures (such as extracellular capsule and “slime”) are reviewed in relation to pathogenicity. The possession of an
Gram positive bacteria have a simpler cell wall, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan is a polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. In effect, the cell wall traps the crystal violet in the cytoplasm, concealing the red dye safranin in gram staining experiment.
Peptidoglycan (murein) is the principal component of the bacterial cell wall and it is responsible for the shape and extreme tough nature of the cell wall. Based on the characteristics of the cell wall, the bacterial cells are classified into Gram Positive and Gram Negative , primarily based on the classical staining reaction called Gram Staining.
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
Cell Wall Staining Procedure Napa Valley College
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
Decolorizing the cell causes this thick cell wall to dehydrate and shrink, which closes the pores in the cell wall and prevents the stain from exiting the cell. So the ethanol cannot remove the Crystal Violet-Iodine complex that is bound to the thick layer of peptidoglycan of gram positive bacteria and appears blue or purple in colour.
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (854.9 KB) Introduction. Gram staining is a fundamental microbiological staining technique that has been in use for more than 160 years, and is usually the first test performed for identification of bacteria. Gram staining is based on the ability of the bacteria cell wall to retain a crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. See Page 2 for a diagram of the Gram-negative cell wall and a video on Gram Staining!
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionic (negative charge). Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on
Bacterial Staining Free Essays PhDessay.com
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
The cell wall of most bacteria has an overall net negative charge and thus can be stained directly with a single basic (positively charged) stain or dye. This type of stain allows us to observe the shape, size and arrangement of bacteria.
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
3) Peptidoglycan (cell wall) Provides bacterial shape and rigidity. The cell wall The cell wall consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
Gram staining begins by adding a crystal violet stain to a bacterial smear and then applying iodine to form a complex that fixes the crystal violet stain within the cell.
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionic (negative charge). Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic Cetylpyridinium chloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
Prokaryotes (bacteria) and Gram Staining
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
The differential Gram stain gives additional information about the bacterial cell wall, which may be Gram positive (the deep purple color of crystal violet), or Gram negative (the pink color of the counterstain safranin).
Prokaryotes (bacteria) and Gram Staining Gram positive and Gram negative. BTEC101, Day 5 Why are we learning this? We will be monitoring our bioreactors for bacterial contamination. We sometimes are culturing E.coli as the organism of choice and in this case we want to make sure it is not contaminated. BTEC101, Day 5 Mycoplasmas Mycoplasmas small prokaryotes without a cell wall. …
about the characteristics of the cell wall (Thickness). Gram staining (or Gram’s Gram staining (or Gram’s method) is an emprical method of differentiating bacterial species into two large
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
Bacterial Staining Free Essays PhDessay.com
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
21/06/2014 · A method to fluorescently stain the surfaces of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial cells compatible with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy is presented. This method utilizes a commercially-available fluorescent probe to label primary amines at the surface of the cell. We
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls, especially of Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The cells are smeared in water on a slide and, as soon as air-dry, are stained 3-4 minutes with a 1 % aqueous solution of new fuchsin.
INTRODUCTION Gram staining is the most essential and universally used staining technique in bacteriology laboratory. Gram-staining was firstly introduced by Cristian Gram in 1883.This method is used to distinguish between gram positive and gram-negative bacteria which have consistent differences in their cell walls. gram-positive bacteria stain
Gram staining is a special technique which is used to stain bacteria. This technique was developed by Christian Gram in 1884. The stain stain used in Gram staining is called Gram stain. Chemically Gram stain is a weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet or gentian violet. On the basis of cell wall structure and its stain ability wit Gram stain, bacteria are grouped into two categories. They
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram bacteria. 4. Gram bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
the comparison between bacterial structures, the cell wall structure and bac-terial flagella could be observed well in the order of PTA, EMstainer, and ura- nium acetate. With TI blue staining, flagella could be observed very poorly. In comparison between bacteria, gram negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, could be observed well as compared with gram …
Phloxine B a versatile bacterial stain Rasooly – 2007
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
Gram Staining Bacteria Cell Wall By Wasim Arsal YouTube
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 Stain Technology Vol 28 No 4
The cell wall also maintains a defined cell shape and plays an integral role in the anchoring of proteins to the cell surface (3, 4). Most Gram-positive cell walls are resistant to dissolution with lysozyme ( 5 ).
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
Bacterial Staining Free Essays PhDessay.com
membranes, cell wall and surface appendages To name the general structures, and polymers that make up bacterial cell walls To explain the differences between gram negative and gram positive cells To describe the chemical composition, function and serological classification as H antigen of bacterial flagella and how they differ from flagella of eucaryotic cells To describe the chemical
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls. A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It’s an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.
RELATIONSHIP OF CELL WALL STAINING TO GRAM
Bacterial Staining Free Essays PhDessay.com
Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
staining and how it differentiates bacteria on the basis of their cell wall structure should also be included (1 point). The purpose and objectives of the experiment should be stated and a …
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls by detecting the properties of peptidoglycan. Gram staining method is useful in differentiating majority of bacterial species into two broad categories. Even though all bacterial species cannot be differentiated based on gram staining technique, this method has immense application in clinical
Prescott’s Microbiology 9 Edition 3 Bacterial Cell Structure
• relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction • compile a list of the structures found in all the layers of bacterial cell envelopes, noting the functions and the major component molecules of each
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
The differential Gram stain gives additional information about the bacterial cell wall, which may be Gram positive (the deep purple color of crystal violet), or Gram negative (the pink color of the counterstain safranin).
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
Facile method to stain the bacterial cell surface for
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC – Download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .ppsx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
staining) 2. The Gram staining classifying two distinct types of bacteria based on structural difference in their cell wall (Gram+ and Gram-) 3. The positive staining is caused by a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Gram+ bacteria. 4. Gram+ bacteria lack outer membrane, and have a thicker peptidoglycan with teichoic acids 5. Many species of Gram-bacteria are pathogenic, causing
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC Scribd
The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them.
Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection
A BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN1 H. L. CHANCE, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Okla. Received for publication Jan. 6, 1953 ABSTRACT.-A new method is given to stain bacterial cell walls,
Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection
The cell wall comprises mainly peptidoglycan, a negatively charged polymer matrix comprising of cross-linked chains of amino sugars, namely, N -acetylglucosamine and N -acetylmu-
Isolation and Solubilization of Gram-Positive Bacterial
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
Prokaryotes (bacteria) and Gram Staining
Techniques of bacterial taxonomy China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Staining •Gram stain (the reaction may alter as the cells age) •Acid-fast staining (strains containing mycolic acids) •Sudan Black staining (stains containing lipophilic cellular inclusions, eg. polyhydroxybutyric acid) •Others (eg. spore staining, capsule staining) physiological and
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 Stain Technology Vol 28 No 4
Automated Gram-staining characterization of bacterial cells using colour and cell wall properties has been carried out by Hiremath and Bannigidad [14] using digital image processing techniques.
Bacterial Cell Wall Differential Staining VMC Scribd
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 Stain Technology Vol 28 No 4
Relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction. 37 . 38 Bacterial Cell Wall • Peptidoglycan (murein) –rigid structure that lies just outside the cell plasma membrane –two types based on Gram stain •Gram-positive: stain purple; thick peptidoglycan •Gram-negative: stain pink or red; thin peptidoglycan and outer membrane . 39 Cell Wall Functions • Maintains shape
A USEFUL BACTERIAL CELL WALL STAIN National Center for
Bacterial Polysaccharide Overview
A Bacterial Cell Wall Stain1 tandfonline.com
Results and reaction: Reaction / Results Principle Samples of Bacteria All bacteria in smear takes stain Simple stains use basic dyes All types of and appears in color of stain which are positively bacteria. Charged. These positive dyes 0 Shape: interact with the slightly 0 Spherical – coca negatively charged bacterial 0 Rod – bacilli cell wall thus lending the color 0 Arrangement : of the
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
CFDA is bacterial cell wall and cell membrane permeable, and hydrolized by esterase of the cell to stay inside of the cell. DAPI, AO, and EB are used for nucleotide staining and are cell wall permeable except for PI. Therefore, using DAPI and PI , it is possible to stain both membrane intact cells and membrane damaged cells simultaneously. Since PI can stain only membrane damaged cells
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
PART I GRAM STAINING OF BACTERIA Weebly
Cell Wall Staining Procedure Napa Valley College
Gram stain is commonly used to assist in bacterial identification. This stain, first developed in 1884, separates bacteria into groups, depending on their reaction to this stain. Bacteria react by testing gram-positive, gram-negative, gram-variable, with the first two groups being the most common. The response of cells to the stain is due to differences in their cell walls. Cell walls of gram
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
Optimization of distinction between viable and dead cells
Prescott’s Microbiology 9 Edition 3 Bacterial Cell Structure
Differential staining of bacteria on Gram staining is due to a) difference in the cell wall layer components of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria b) difference in the cell structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
Bacterial cells.pdf Bacteria Staining Scribd
•use fresh cultures for light microscopy & staining! 2 Arrangements Binary fission without complete separation diplo-pairs staphylo-grapelike strepto-chains clusters TYPICAL PROKARYOTIC CELL The Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane in nearly all bacteria • Two important functions: – Maintains characteristic cell shape – Prevents the cell from bursting when fluids flow into the
Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection
Automated Gram-staining characterisation of bacterial
Cell wall staining by Chances method generalmicroscience.com